Table of Contents
Introduction
Dyspnea on exertion is shortness of breath and difficulty of breathing. It can be defined as “air hunger” or the sensation of having the urge to breathe, which is caused by a lack of oxygen in the bloodstream. dyspnea on exertion disease the most common symptom of COPD.
Dyspnea is a term used to characterize a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that consists of qualitative distinct sensation that varies intensively.
The experience derives from the interaction among multiple phycological social and environmental factors and may induce secondary histological and behavioral responses. dyspnea may or may not be associated with hypoxemia tachypnea or orthopnea.
Definition of Dyspnea on Exertion
Dyspnea on exertion refers to the sensation of breathlessness or difficulty in breathing experienced during physical activity or exertion. While it’s normal to feel slightly winded during vigorous exercise, dyspnea on exertion goes beyond the expected level of breathlessness, often causing discomfort or distress.

It can manifest as shortness of breath, rapid breathing, or a feeling of suffocation, hindering one’s ability to perform daily tasks or engage in physical activities.
Importance of Recognizing and Addressing Dyspnea on Exertion
Recognizing dyspnea on exertion is crucial as it serves as a vital warning sign of underlying health issues such as cardiovascular diseases, respiratory disorders, or deconditioning. Ignoring dyspnea on exertion may lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment, potentially exacerbating the underlying condition and reducing quality of life.
Addressing it promptly through medical evaluation and intervention can help identify the root cause and implement appropriate management strategies, ultimately improving outcomes and enhancing overall well-being.
In this article, we will explore the various causes of dyspnea on exertion, ranging from common conditions like asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) to more serious cardiac conditions such as heart failure and coronary artery disease.
We will also discuss diagnostic approaches, including medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests like pulmonary function tests and imaging studies.
Symptoms and Clinical Presentation of Dyspnea on Exertion
Gradual Onset vs. Acute Onset
Dyspnea on exertion may manifest gradually over time or suddenly (acute onset). Gradual onset dyspnea often indicates chronic conditions such as heart failure or COPD, while acute onset could signify an acute event like a pulmonary embolism.
Severity and Frequency
The severity and frequency of dyspnea episodes vary depending on the underlying cause and individual factors. Some may experience mild breathlessness with exertion, while others may struggle to breathe even during minimal activity. Understanding the pattern of dyspnea helps healthcare providers in diagnosis and management.
Associated Symptoms

Check normal level of hypertension value its very important to know.
Exploring the Causes of Dyspnea on Exertion
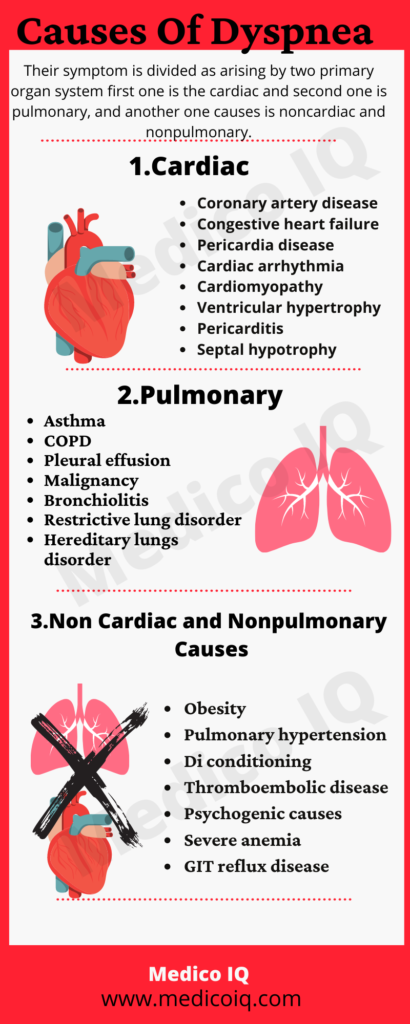
Dyspnea on exertion can stem from a variety of underlying health conditions, ranging from cardiac and pulmonary disorders to other contributing factors. Understanding these causes is pivotal in identifying and addressing the root issue effectively.
Cardiac Causes
Pulmonary Causes
Other Causes
Diagnosis of Dyspnea on Exertion
A thorough diagnostic approach is crucial in identifying the underlying cause of dyspnea on exertion and guiding appropriate treatment interventions.
Medical History and Physical Examination
Gathering a comprehensive medical history, including symptoms, duration, exacerbating factors, and past medical conditions, coupled with a thorough physical examination, provides valuable clues to the underlying aetiology of dyspnea on exertion.
Diagnostic Tests

Differential Diagnosis
Considering a broad range of potential causes, including cardiac, pulmonary, hematological, and metabolic disorders, helps differentiate between various etiologies and formulate an appropriate treatment plan.
By employing a systematic approach to diagnosis, healthcare providers can effectively identify the underlying cause of dyspnea on exertion, facilitating timely intervention and improving patient outcomes.
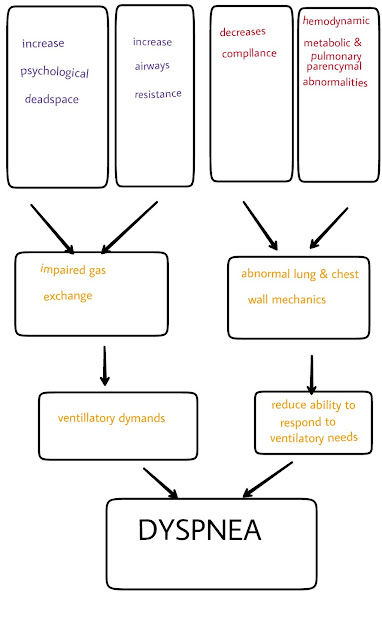
Pathophysiology
The pathophysiology of dyspnea on exertion is complex and has not been completely elucidated. Although dyspnea is a relatively common problem, the psychophysiology of the uncomfortable sensation breathing is poorly understood.
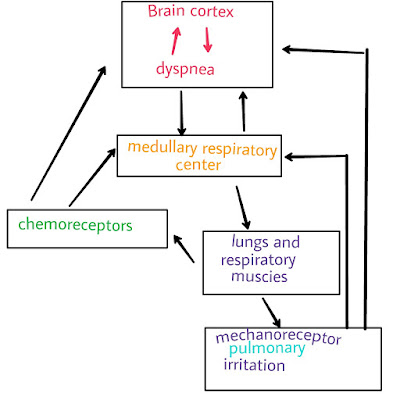
The respiratory center in the medulla controls breathing dyspnea as the result of cortical stimulation. The experience of dyspnea likely results from a complex interaction between chemoreceptor stimulation, mechanical abnormalities in breathing, and the perception of those abnormalities by the CNS.
Dermatitis of blood gases detected by both lungs and central chemoreceptor and stimulation of lungs and respiratory muscle mechanoreceptor stimulate the respiratory center.
Mechanoreceptor responds to stretch and also have a demonstrated effect on the medullary respiratory center stimulate the cerebral cortex directly contributing to the action of dyspnea.
Management and Treatment Options
Managing dyspnea on exertion requires a multifaceted approach aimed at addressing underlying conditions, improving functional capacity, and enhancing overall quality of life. In this article, we explore various management and treatment options tailored to alleviate breathlessness during physical activity.
Lifestyle Modifications

You should do somatic yoga for healthy lifestyle : Read how to do somatic yoga
Medications for Dyspnea on Exertion
Surgical Interventions
Non-Pharmacological Treatment

Pulmonary Rehabilitation Programs
Structured pulmonary rehabilitation programs incorporate exercise training, education, and psychosocial support to improve exercise tolerance, alleviate dyspnea, and enhance the quality of life in individuals with chronic respiratory conditions.
Patient Education and Support
Empowering patients with knowledge about their condition, self-management strategies, and resources for support can foster adherence to treatment plans and enhance overall well-being.
In conclusion, the management of dyspnea on exertion encompasses a comprehensive approach involving lifestyle modifications, medications, surgical interventions, rehabilitation programs, and patient education. By addressing underlying factors and optimizing treatment strategies, individuals can experience significant relief from breathlessness and achieve better health outcomes.
Understanding Prognosis and Potential Complications
Impact on Quality of Life
Dyspnea on exertion can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, affecting their ability to engage in daily activities and enjoy a fulfilling lifestyle.
The constant struggle for breath during physical exertion can lead to anxiety, frustration, and limitations in social interactions and recreational pursuits.
Furthermore, the fear of breathlessness may result in avoidance of activities, further exacerbating physical deconditioning and diminishing overall well-being.
Long-term Outlook
The long-term outlook for individuals experiencing dyspnea on exertion depends largely on the underlying cause and the effectiveness of management strategies implemented. For some, lifestyle modifications, medication, and rehabilitation programs may alleviate symptoms and improve functional capacity, allowing for a relatively normal life.
However, in cases of progressive conditions such as advanced heart failure or severe pulmonary disease, the prognosis may be more guarded, requiring ongoing medical management and support to maintain quality of life.
Potential Complications
Complications associated with dyspnea on exertion can arise from both the underlying condition and its impact on physical and mental health. Chronic respiratory conditions like COPD or asthma may lead to recurrent exacerbations, respiratory infections, and pulmonary hypertension if left uncontrolled.
Similarly, cardiac disorders such as heart failure or coronary artery disease increase the risk of arrhythmias, myocardial infarction, and stroke, further complicating the clinical course. Moreover, the psychological toll of living with dyspnea, including anxiety, depression, and social isolation, can exacerbate symptoms and impede effective management.
In conclusion, understanding the prognosis and potential complications of dyspnea on exertion is essential for healthcare providers and individuals alike. By addressing underlying conditions, optimizing treatment strategies, and providing comprehensive support, it is possible to improve outcomes, enhance quality of life, and minimize the impact of dyspnea on exertion on overall health and well-being.
FAQs
What is dyspnea on exertion?
Dyspnea on exertion refers to difficulty breathing or breathlessness experienced during physical activity or exertion. It may manifest as shortness of breath, rapid breathing, or a feeling of suffocation.
What causes dyspnea on exertion?
Medical history and physical examination
Complete blood count and metabolic panel
An achy x-rays
Arterial blood gas analysis
ECG and echocardiography
CT scanning
Bronchoscopy
Exercise treadmill testing
What causes dyspnea on exertion?
Dyspnea on exertion can be caused by various underlying health conditions, including cardiovascular diseases such as coronary artery disease and heart failure, respiratory disorders like asthma and COPD, as well as other factors such as obesity, anaemia, and deconditioning.
When should I be concerned about dyspnea on exertion?
It’s essential to pay attention to dyspnea on exertion, especially if it is new, persistent, or progressively worsening. If you experience sudden or severe shortness of breath, chest pain, or dizziness during exertion, seek medical attention promptly.
How is dyspnea on exertion diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as pulmonary function tests, imaging studies (chest X-ray, CT scan), cardiac tests (echocardiogram, stress test), and blood tests (complete blood count, arterial blood gas).
What are the treatment options for dyspnea on exertion?
Treatment depends on the underlying cause but may include lifestyle modifications (exercise, weight management, smoking cessation), medications (bronchodilators, diuretics, beta-blockers), surgical interventions (coronary artery bypass grafting, valve replacement), pulmonary rehabilitation programs, and patient education and support
Can dyspnea on exertion be prevented?
While it may not always be preventable, adopting a healthy lifestyle, managing chronic health conditions, staying physically active, and avoiding smoking can reduce the risk of developing dyspnea on exertion or alleviate its severity.
Is dyspnea on exertion a sign of a serious medical condition?
Dyspnea on exertion can be a symptom of various serious medical conditions, including heart and lung diseases. Therefore, it is essential to undergo proper evaluation by a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.